Table of Contents
Introduction to SAP EWM
SAP Extended Warehouse Management is software that allows companies to efficiently manage their warehouse operations, controlling outbound and inbound processes and identifying things stored in storage facilities, which in turn improves the efficiency of the supply chain. SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) helps improve supply chain and logistics by ensuring a solid warehouse structure to ensure smooth operations.
What is SAP EWM Warehouse Structure?
SAP EWM allows you to create as well as manage the warehouse’s layout using amazing accuracy. It breaks the warehouse into components that are logical to ensure the smooth movement of goods along with the storage process. Here’s how it is usually structured:
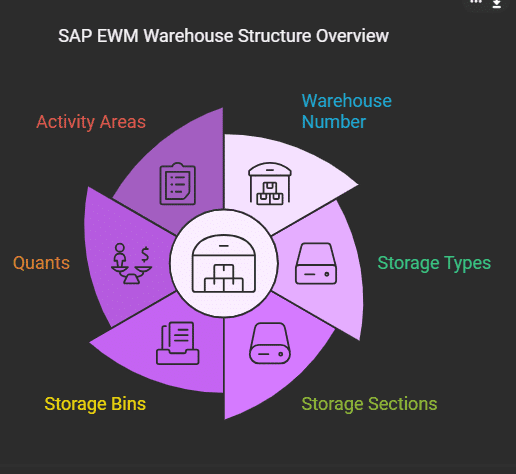
- Warehouse Number: The top-level unit of organization within SAP EWM. It covers the entire physical warehouse.
- Storage Types: These are subdivided areas within the warehouse that represent areas such as the bulk storage area, the picking areas and cold storage. Each storage type has distinct handling guidelines.
- Storage Sections: Further subdivided storage kinds. For instance, in an area for cold storage, you could have separate sections for frozen as well as chilled items.
- Storage Bins: The smallest component in the structure of warehouses. Each bin is a distinct area where goods are kept, tracked with bin numbers.
- Quants: This is where magic occurs! Quants represent the inventory inside the specific bin. Each quant is a distinct combination of batch, product batch and quantity. By tracking quants, SAP EWM ensures:
- The numbers of the same bin will be identical.
- Accurate tracking of materials at the smallest granularity.
- Support for processes such as the removal of stock put away as well as physical inventory.
- Activity Areas: Logical groups of bins to perform specific tasks like pick, putaway or inventory tracking.
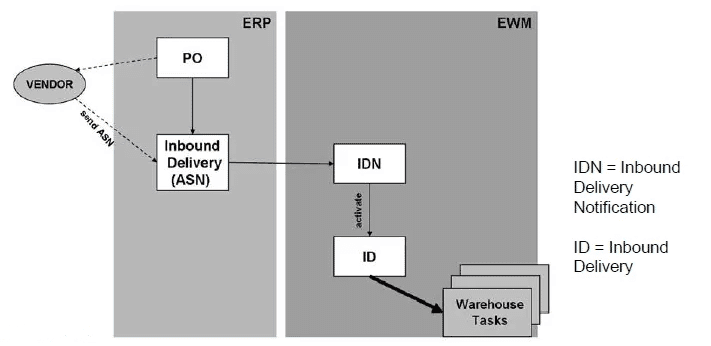
Image courtesy:SAP
Deployment Options of SAP EWM
SAP EWM can be implemented using SAP S/4HANA in two distinct ways.
There are two variants of this system. The base EWM system with basic capabilities and options are available in SAP S/4HANA license.
- Advanced EWM has enhanced features, but it also requires additional licensing.
- Decentralized EWM for SAP S/4HANA. This stand-alone application can be connected directly to SAP S/4HANA, providing seamless transactions. This is an ideal solution for large-scale material flow and warehouse systems since it is seamlessly integrated through remote functions (RFCs) and Core Interface Functions (CIFs).
Key Features and Capabilities of SAP EWM
SAP EWM contains many features to help make warehouse management more efficient like:
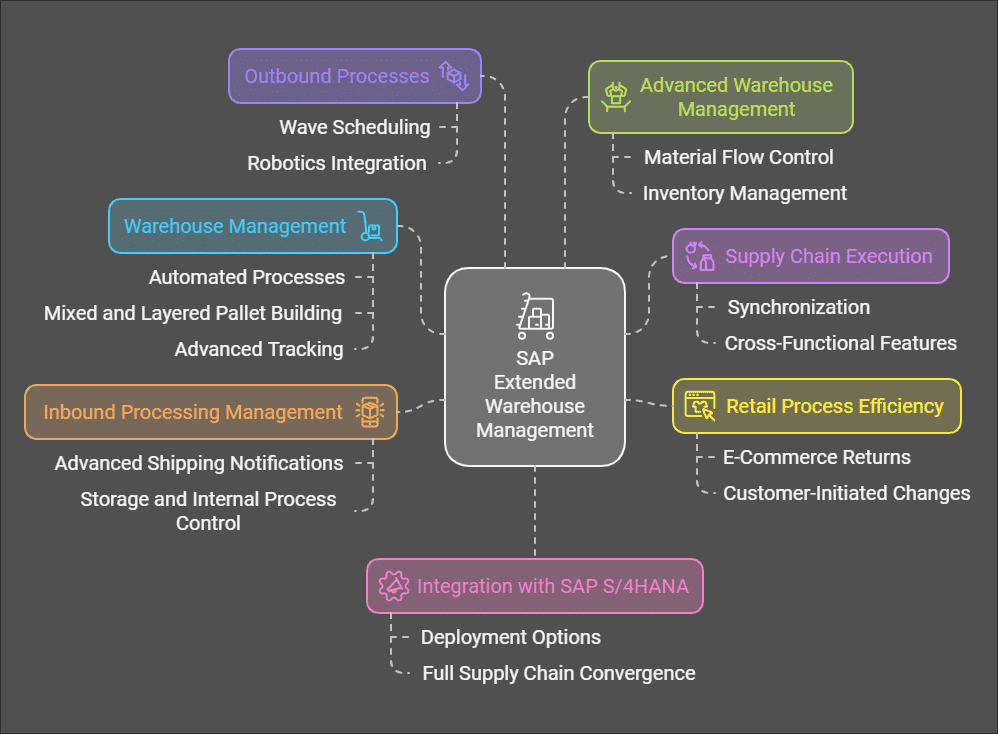
SAP EWM facilitates efficient control over warehouse-related activities like posting, picking or bin management. The software can alert you to system changes quickly and allows quick corrective actions to be taken swiftly.
Slotting and deconsolidation EWM provides slotting to maximize the distribution of products in warehouses and deconsolidation that separates MHUs that are mixed (MHUs) into storage sections.
The SAP EWM Labor Management feature allows it to track and plan employees’ productivity and their use of resources that directly impact efficiency in operations. Additionally, it provides a variety of options to help make the management of warehouses more efficient, the most notable ones being:
Organizational Structure of SAP EWM
An organized warehouse structure is essential to successful operations. Here are the main elements of SAP EWM:
The client is a crucial component of every program; the customer holds all the vital data needed to keep warehouse data. The company code and the company, also known as its code of business, contain financial statements describing its operations.
Plant (the physical space that functions as a trading or manufacturing facility responsible for acquiring delivering, planning, and storing products). Storage Place is the area inside an industrial facility that is used to track the individual materials in stock.
Warehouse numbers are the most advanced degree of organization in the SAP EWM System. Bins that are used for storage as well as other models assist in organizing the items at the back of warehouses. Additionally, the SAP EWM organization framework helps to ensure efficient task management as well as the continuous flow of products and supplies, resulting in the most efficient warehouse system.
Activity Areas and Work Centers in SAP EWM
Activity Areas within SAP EWM provide an efficient way to organize storage bins logically for different tasks such as picking, putting away inventory, replenishment, etc. By organizing similar bins into Activity Areas to serve such functions as picking, putting away, replenishment, or inventory, we enhance warehouse operations by streamlining tasks efficiently. Activity Areas improve warehouse operations while increasing efficiency by dividing aisles or rows into levels, forming logical activity areas.
Work centres are essential in warehouses for tasks like packing, deconsolidation, and quality inspections, each with its own procedures to ensure the timely completion of each task.
Deployment Advantages of SAP EWM
SAP EWM allows businesses both decentralized and embedded deployment to meet their specific business needs. The ability of decentralized EWM to operate independently makes it a great option for warehouses that require high-performance volume handling. embedded EWM provides cost-effective options that leverage SAP S/4HANA’s already.
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
Businesses using SAP EWM report significant enhancements in warehouse operations:
Improved storage space utilization Businesses that employ slotting techniques using SAP EWM have reported an approximately 20% reduction in the utilization of storage space. Slotting assists in arranging items according to the demand of customers to improve space management.
Resource Optimization: Using features for managing labor, an important FMCG company was able to increase the allocation of warehouse labour by 15%, resulting in increased productivity of workers because of improved management and visibility of the assignments of work.
Improved accuracy of inventory: By using ERP EWM’s inventory physical capabilities One retailer achieved almost 99% accuracy in the stock data. By utilizing specific storage areas and areas for staging, the inventory audits were more accurate and transparent.
Conclusion
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) is more than just an additional warehouse management tool. It can be utilized to achieve efficiency in operations and the strategic goals of logistical management. From advanced slotting features to more efficient organization structures, EWM gives businesses the tools needed to thrive in today’s complicated supply chain.
Companies that wish to increase their warehouse operations can benefit from SAP EWM, a robust tool that provides total control, a wide range of options for rollout, and other features that produce tangible business results. SAP EWM proves its worth in modern warehouses by managing outbound and inbound activity management, as well as coordinating the most challenging warehouse tasks effectively and ensuring that they are completed
You might also like the below articles.
- sap s4hana migration
- GST E invoice
- understanding abap objects
- clean core sap
- SAP interfaces
- Joule ai copilot
- Mastering sap background job processing
- SAP Ewm tcodes a handy guide
- object oriented programming in sap abap
- understanding sap license costs
- SAP Datasphere
- industry4.0 with sap
- Condition contract management in sap s4 hana
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap
- ethical ai development