Table of Contents
Introduction to SAP EWM Integration
Smooth, efficient logistics play a crucial role in the success of businesses dealing with
high shipment volumes. SAP’s Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) system and the Transportation
The management system offers a fully integrated solution for managing warehouse and transportation
logistics. Direct integration of these systems increases outbound logistics by automating key activities such as planning, packaging, and loading.
Integration between SAP EWM and logistics operations cannot be overstated as it streamlines processes and enhances efficiency across all of them.
This blog explores the integration of SAP EWM with TM, showing its essential configurations and highlighting its advantages for businesses that wish to make their processes more streamlined and efficient. Creating direct connections between SAP EWM and TM platforms is essential in order to harness their full value potential.
SAP EWM and TM
SAP EWM integration is a powerful solution for warehouse operations management, including inventory control. It empowers companies with the necessary functionalities to optimize internal processes and gain real-time visibility into warehouse activities. SAP TM optimizes transportation processes, supporting route planning, freight unit management, carrier selection, and shipment tracking, enhancing communication and data flow between warehouse and transportation operations for effective outbound logistics.
This integration process clearly demonstrates the effectiveness of SAP EWM integration in optimizing logistics operations.
Direct Integration Process
The direct integration process of SAP EWM with TM directly automates some steps in outbound
logistics. Below is an elaborate overview of this process:

- Creation of Sales Order:
o First, the process begins with the generation of a sales order in SAP TM. The sales
order comprises all the details that are essential for planning deliveries outwards. - Freight Order and Packaging:
o Freight orders are created from sales orders. These orders specify
delivery locations and dates.
Packaging units are calculated with the help of SAP TM’s Package Building functionality.
which takes into account the dimensions, weight, and stacking of products. This
ensures that packaging materials and space are used to their fullest potential. - Loading Sequence Determination:
o SAP TM determines the most efficient loading sequence for HUs.
This sequence is determined by the priority of delivery, capacity of the vehicle, and customer demands. - TU Creation in SAP EWM
o Some integration signals from SAP TM initiate the automatic creation of TUs in SAP EWM. The Units will collate and arrange for the shipment of the good. - HUs Management
o In SAP EWM, it uses PSHUs as a standard reference to direct picking and pack processes. This way, it eliminates any error or inefficiency that may occur during the warehouse process. - Yard Management:
The movement of TUs inside the yard is managed using SAP EWM’s Yard
Management functionality. This step smoothes out the transition from warehouse
to loading docks. - Goods Loading and Issue:
o HUs are loaded to the vehicles using the loading sequence from SAP TM.
o It is finally ended by posting of Goods Issue which completes the entire
outbound process successfully.
For direct integration, certain parameters must be configured in both SAP TM and EWM.
These configurations ensure smooth communication and automatization of processes.
TM Setup: - Freight Unit Type Definition:
o Defines freight unit types to standardize shipment handling.
o Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Planning → Freight Unit → Define
Freight Unit Types. - Freight Unit Building Rule:
o Builds rules for automated freight unit building.- Transaction: /N/UI2/FLP → Home → Transportation Profiles & Settings → Create
- Control Keys for Document Integration:
- Define control keys to allow easy communication between SAP TM and EWM.
- Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Integration → Logistics Integration→ Define Control Keys for Document Integration.
- Logistics Integration Profile:
o Define profiles for logistics data exchange management.
o Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Integration → Define Logistics Integration Profile. - Transportation-Relevance of Delivery Documents:
- No Assign which of the delivery documents is relevant for transportation.Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Integration → Define Transportation-Relevance of Delivery Documents.
- EWM Integration Profile:
No Activate profiles in order to facilitate the integration to SAP EWM Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Integration → Define EWM Integration Profile. - Freight Order Type:
No Activate freight order types in order to immediately allow processing.Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Freight Order Management →Definition Freight Order Types. - Means of Transport:
- Create transport vehicles and compartments. Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Master Data → Resources → Define Means of Transport.
- Unified Package Building:
- Set up package building profiles to streamline the building process.
- Path: SIMG → Transportation Management → Planning → Unified Package Building → Define Unified Package Building Profile.
EWM Setup:
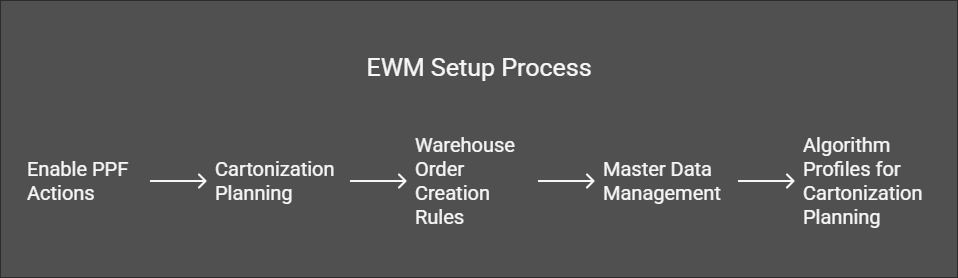
- PPF Actions: Enable Post Processing Framework (PPF) actions to carry out processes like TU generation and synchronization. o Transaction: SPPFCADM.
- Cartonization Planning:
o Define algorithm profiles and process profiles for cartonization to automate
PSHU creation. Path: SCM → Extended Warehouse Management → Goods Issue Process →
Cartonization Planning. - Warehouse Order Creation Rules:
o Configure rules for generating warehouse orders linked to PSHUs.Path: SCM → Extended Warehouse Management → Cross-Process Settings → Warehouse Order. - Master Data Management:
o Assign packaging materials to transport means and maintain location data.Transaction: /N/SCWM/PM_MTR. - Algorithm Profiles for Cartonization Planning:
Determine algorithm profiles for cartonization. Transaction: /N/SCWM/CAPPDET.
Advantages of Direct Integration
In conclusion, mastering SAP EWM integration is imperative for businesses aiming to excel in logistics and supply chain management.
The direct integration of SAP EWM integration and TM has many advantages that can significantly enhance operational effectiveness:
- Smooth Operations: Automated processes reduce manual effort and operational delays.
- Improved Accuracy: Real-time data exchange minimizes errors in picking, packing, and loading activities.
- Resource Optimization: Efficient loading sequences ensure optimal use of vehicles and storage space.
- Increased Visibility: Integrated systems offer end-to-end tracking of shipment and inventory.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimized overhead process results in significant cost savings.
- Scalability: The integration handles critical logistics scenarios and can be easily used by
- business of all sizes.
Conclusion
The integration of SAP EWM with TM significantly improves businesses’ outbound logistics. SAP EWM integration automates key processes, minimizes errors, and efficiently utilizes resources, giving companies a competitive edge in the market. By using SAP EWM and TM capabilities, businesses can achieve operational excellence and superior customer experiences.
You might also like the below articles.
- Yard management in sap ewm
- sap project intelligence network
- advanced production integration with sap ewm
- Credit management comparison of sap fscm
- SAP EWM
- sap s4hana migration
- GST E invoice
- understanding abap objects
- clean core sap
- SAP interfaces
- Joule ai copilot
- Mastering sap background job processing
- SAP Ewm tcodes a handy guide
- Object-oriented programming in sap abap
- understanding sap license costs
- SAP Datasphere
- industry4.0 with sap
- Condition contract management in sap s4 hana
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap
- ethical ai development