Table of Contents
Introduction SAP Migration
Businesses switching to new SAP systems like SAP S/4HANA or going to the cloud depend critically on SAP migration. It minimizes disturbance and guarantees operational continuity by use of data, configuration, and customizing elements from legacy systems.
This blog explores the key aspects of SAP migration, including data types to migrate, step-
by-step configurations, tools, common errors, and technical considerations.
Data Types to Migrate in SAP
SAP migration requires transferring several critical data types. Each type ensures smooth
business operations post-migration.
Master Data:
Master data is foundational and used across modules. It is relatively stable and essential for
business processes.Examples: Customer Master, Material Master, Vendor Master, Cost Center Master Why migrate it? Ensures consistent and accurate operations across systems.
Transactional Data:
Transactional data reflects actual business activities and is crucial for continuity. Examples: Sales Orders, Purchase Orders, Invoices, Goods Movements, Why migrate it? Maintains ongoing processes like order fulfillment and financial reporting.
Configuration Data:
Configuration data dictates system behavior and business processes.Examples: Organizational Structures, Document Types, Pricing Conditions, Tax Settings, Why migrate it? Ensures that processes function as expected in the new system.
Custom Code and Customizing:
Customizing includes modifications like user exits or custom programs tailored to specific needs.Examples: User Exits, Badis (Business Add-Ins), Custom Reports ,Why migrate it? Revalidate and adjust custom code to ensure compatibility with the target system.
Open Items:
Open items include pending or incomplete transactions.Examples: Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Open Purchase Orders Why migrate it? Ensures financial accuracy and prevents process disruption.
Historical Data:
Historical data is no longer active but necessary for compliance and reporting. Examples: Archived Financial Transactions, Inventory Data, Why migrate it? Supports regulatory requirements and long-term reporting.
Step-by-Step SAP Migration Configuration
The SAP migration process involves detailed planning and execution. Here is a
comprehensive guide:
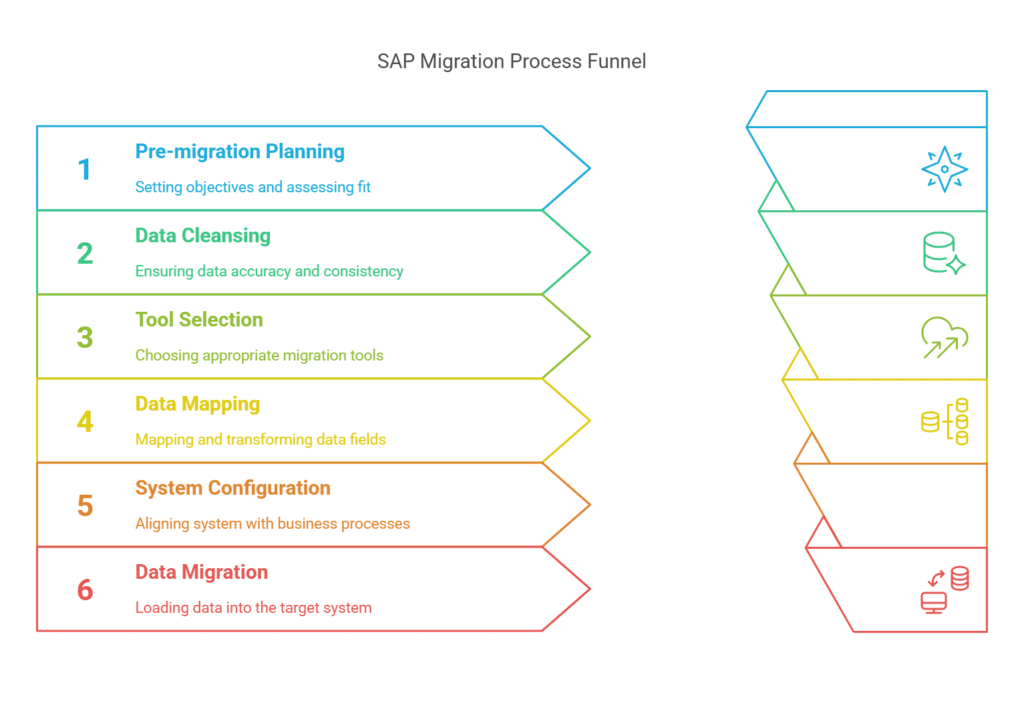
Step 1:Pre-migration Planning and Evaluation
Analyze the source system then specify migration objectives.Activities: List the systems involved, assess fit, and specify the migration extent.
Step 2: Data Cleansing and Profiling
- Objective: Ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Tasks: Use tools like SAP Data Services to clean data, address duplicates, and standardize formats.
Step 3: Choose the Right Migration Tools
- Objective: Select tools that match your migration scenario.
Examples:- SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit for ECC to S/4HANA migration.
- SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT) for real-time data replication.
Step 4: Data Mapping and Transformation
- Objective: Map source data fields to target structures.
- Tasks: Define mapping rules and handle transformations like currency conversion.
Step 5: System Configuration
- Objective: Align the target system with business processes.
- Tasks: Recreate organizational structures and document types in SAP S/4HANA.
Step 6: Data Migration
- Objective: Load data into the target system.
- Tasks: Perform incremental loads and monitor for accuracy.
Step 7: Testing and Validation
- Objective: Verify that moved data and settings operate as intended.
- Tasks: Conduct unit, integration, and automated testing.
Step 8: Go-Live and Post-Go-Live Support
- A transition to the new system that causes as little interruption as possible is the goal.
- Tasks: Implement a cutover plan and provide ongoing support.
Best Tools for SAP Migration
A successful migration depends on choosing appropriate tools. Here are the top tools:

SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit
- Optimal for: Migration from ECC to S/4HANA.
- Key Features: Integration with SAP Data Services, automated processes, and preconfigured migration content.
SAP Data Services
- It works well for data loading, transformation, and extraction (ETL).
- Key Features: Facilitates profiling, data cleaning, and large-scale migration.
SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT)
- Best For: Real-time or batch data replication.
- Key Features: Synchronizes data between SAP and non-SAP systems.
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI)
- Best For: Cloud integrations.
- Key Features: Pre-built templates, scalable flows, and secure cloud-to-cloud integrations.
SAP Solution Manager
- Best For: System monitoring and configuration management.
- Key Features: Centralized setup, testing tools, and solution monitoring.
Common Errors in SAP Migration and Solutions
Data Integrity Issues
- Error: Data corruption or mismatched fields.
- Solution: Use data profiling tools and perform thorough testing.
Configuration Inconsistencies
- Error: Misaligned configurations between systems.
- Solution: Document configurations and validate with SAP Solution Manager.
Extended Downtime
- Error: Prolonged system unavailability during migration.
- Solution: Adopt phased migration strategies and tools like SLT.
Custom Code Compatibility Issues
- Error: Legacy customizations may not work in the new system.
- Solution: Use SAP Compatibility Check to identify and update incompatible code.
Technical Details to Consider During SAP Migration
- System Compatibility: Ensure source and target systems are compatible, especially when migrating to S/4HANA or the cloud.
- Database Optimization: Optimize schemas for HANA’s in-memory architecture.
- Custom Code Adjustments: Update ABAP code for deprecated functions.
- Data Validation: Use automated scripts to confirm data consistency post-migration.
Conclusion
A difficult but worthwhile operation, SAP migration calls for careful planning, tool choice, and execution. Businesses may make a flawless transformation by knowing the kinds of data involved, applying a disciplined configuration process, and utilizing the right technologies.
Correct preparation and testing help to minimize common problems including data integrity concerns and downtime. SAP’s sophisticated technologies and best practices let companies upgrade their systems, improve productivity, and open fresh development prospects.
What tools are available for SAP Migration?
SAP offers various tools for SAP migration, such as the SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit, SAP Data Services, and SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT), which automate and streamline the process. Ensuring data quality during migration involves thorough cleansing, validation, and testing, with automated tools and multiple test runs ensuring data integrity.
How long does an SAP Migration project typically take? What support is available from SAP during migration?
An SAP Migration project typically takes a few months to over a year, depending on the complexity and scope of the migration. A detailed project plan and timeline should be established during the planning phase. SAP offers various support options, including documentation, training, consulting services, customer support, and community forums.
Can I migrate custom developments and enhancements? What are the common challenges in SAP Migration?
Custom developments and enhancements can be migrated to SAP, but common challenges include data compatibility issues, system downtime, user training, and managing change within the organization. Tools like SAP S/4HANA Custom Code Migration can help with this process, requiring proper planning, risk management, and stakeholder engagement.
You might also like the below articles.
- sap ewm integration
- sap project intelligence network
- advanced production integration with sap ewm
- Credit management comparison of sap fscm
- SAP EWM
- sap s4hana migration
- GST E invoice
- understanding abap objects
- clean core sap
- SAP interfaces
- Joule ai copilot
- Mastering sap background job processing
- SAP Ewm tcodes a handy guide
- Object-oriented programming in sap abap
- understanding sap license costs
- SAP Datasphere
- industry4.0 with sap
- Condition contract management in sap s4 hana
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap
- ethical ai development