Table of Contents
SAP SD Pricing – Questions & Answers
1. Why do we assign a condition type in transaction OVKK, and what is its significance in SAP SD Pricing?
- The Condition Type is assigned in OVKK to link pricing procedures with sales areas.
- Ensures correct pricing procedure selection based on sales org, distribution channel, and division.
- T-Code: OVKK
2. What is the function of the Exclusion Indicator in SAP SD pricing?
- The Exclusion Indicator prevents SAP from applying a condition if another condition is met.
- Helps in condition comparison (e.g., Best of two discounts).
3. What is the common transaction code (T-Code) used for pricing configuration in SAP?
- Most Common T-Codes:
- VOKO
- V/06 – Condition Type Configuration
- V/08 – Pricing Procedure Configuration
- VK11 – Condition Record Maintenance
4. What is a condition supplement, and how is it used in SAP SD pricing?
- A condition supplement is an additional condition that applies automatically when a primary condition is met.
- Example: A base price (PR00) includes a mandatory surcharge (KP00).
- Supplements are maintained in VK11.
5. What is Condition Update, and how does it impact pricing?
- Condition Update allows SAP to limit condition usage based on specific criteria (e.g., quantity, value, or time period).
- Ensures promotional discounts apply only within defined limits.
- Once the limit is reached, the discount automatically stops.
- T-Code: V/06 → Condition Type → Activate Condition Update
6. Does SAP restrict the number of orders in a condition update?
- Yes, SAP can restrict the number of orders using condition updates.
- Example: A discount (10% off) applies only for the first 100 orders. Once the limit is reached, the system ignores the condition.
7. Which Info Structure is used for the Condition Update process?
- S074 is the standard Info Structure used for condition updates in SAP.
8. What happens if the “Group Condition” indicator is checked in pricing?
- If Group Condition is checked, SAP applies the pricing condition based on the total quantity across all items in the order.
- Useful for bulk discounts and cumulative pricing.
- Example: Buy 100 units across multiple items, get a 5% discount on the total.
9. What is a Group Condition Routine, how many routines exist, and what is their purpose?
- A Group Condition Routine defines how a group condition is calculated in pricing.
- Used for volume-based pricing.
- There are multiple routines available in V/08 (Pricing Procedure).
- Common Routine Examples:
- 1 – Overall Document
- 2 – Across all condition types, etc.

10. What is Rounding Difference Comparison, and why is it relevant in pricing?
- Rounding Difference Comparison ensures that pricing rounding differences are handled correctly.
- Avoids minor currency mismatches in invoices.
- Helps maintain accurate price calculations.
Additional SAP SD Pricing Concepts
1. What is the Condition Technique in SAP, and what are its key components?
- The Condition Technique is a framework used in SAP for pricing, free goods, output determination, etc.
- Helps determine the correct price based on predefined rules.
- Key Components:
- Condition Table – Stores condition records.
- Access Sequence – Searches for condition records.
- Condition Type – Defines pricing elements (e.g., PR00, KO04).
- Pricing Procedure – Defines the sequence of condition types.
2. What is an access sequence, and how does it determine pricing?
- Access Sequence is a search strategy used to find the correct condition record from condition tables.
- It searches step-by-step until it finds a valid condition record.
- If a condition is found, the search stops (unless “Exclusive” is unchecked).
- Used in pricing, free goods, output, and text determination.
- T-Code: V/07
3. What happens if the “Exclusive” indicator in an Access Sequence is unchecked?
- If “Exclusive” is unchecked, SAP will continue searching through all access levels, even if it finds a valid condition record.
- Multiple condition records may be considered.
- Useful if you want SAP to check all possible pricing records and apply the most relevant ones.
4. What happens if the “Exclusive” indicator in an Access Sequence is checked?
- If “Exclusive” is checked, SAP will stop searching as soon as it finds the first valid condition record.
- Improves performance by reducing unnecessary searches.
- Only the first valid condition record is applied.
- Best Practice: Use “Exclusive” when you only want one valid condition to be applied.
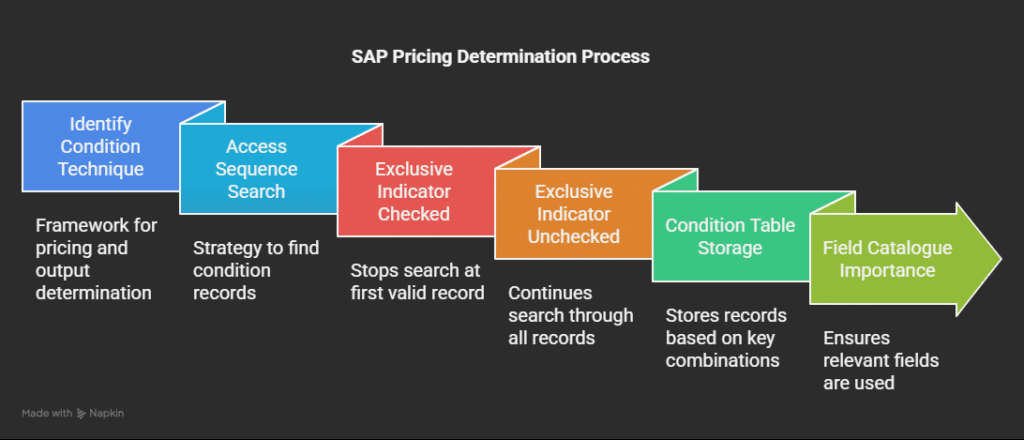
5. What is a Condition Table, and how does it store pricing data?
- A Condition Table is a database table that stores condition records based on key combinations (e.g., Customer + Material, Sales Org + Material Group).
- Condition records are created in VK11.
- T-Codes:
- V/03 (Create)
- V/04 (Change)
- V/05 (Display)
6. What happens if a Condition Table is saved in a local object?
- If a Condition Table is saved in a local object, it will not be transportable to other SAP systems (e.g., from Development → Quality → Production).
- Works only in the current system.
- Best Practice: Always assign it to a transport request for system-wide availability.
7. In which type of request is a Condition Table stored in SAP?
- A Condition Table is stored in a Workbench Request, which allows it to be transported across SAP landscapes (Development → Quality → Production).
- T-Code to check transport request: SE09 / SE10
8. What is the Field Catalogue in SAP SD Pricing, and why is it important?
- The Field Catalogue is a predefined list of fields available for creating Condition Tables.
- Ensures only relevant fields are used in pricing conditions.
- Helps in customizing price determination without modifying SAP tables.
9. What happens if a required field is not available in the Field Catalogue?
- If a field is missing from the Field Catalogue, you must add it manually to the pricing structures.
10. What is the purpose of the Condition Index in pricing determination?
- The Condition Index enables faster searching of condition records across different condition tables.
- Helps in reporting & analysis of pricing data.
- Can be activated in condition type settings (V/06).
- Useful for searching expired or obsolete pricing records.
- T-Code: V/06 (Access Sequence) → Set Condition Index
You might also like the below articles.
- SAP TM Transaction codes
- ethical ai development
- sap migration data configuration tools
- simplifying sap s4hana custom code migration
- sap ewm integration
- sap project intelligence network
- advanced production integration with sap ewm
- Credit management comparison of sap fscm
- SAP EWM
- sap s4hana migration
- GST E invoice
- understanding abap objects
- clean core sap
- SAP interfaces
- Joule ai copilot
- Mastering sap background job processing
- SAP Ewm tcodes a handy guide
- Object-oriented programming in sap abap
- understanding sap license costs
- SAP Datasphere
- industry4.0 with sap
- Condition contract management in sap s4 hana
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap